club foot horse cause
Unless there is a bony deformity of the foot that is causing the bone to be misshapen these cases are caused by soft tissue contraction from limited range of motion andor weight bearing in the affected limb. There is usually a reason for a horse to have mismatched feet whether it be due to conformation lameness foot disease or poor foot care Eggleston says.
So Called Club Foot By James R Rooney Dmv
An injury to the foot is a common cause of clubfoot since it may cause a horse to shift weight to the toe to compensate for pain elsewhere.

. A diet rich in calories and sugar can cause problems as well. Frequently there is mild flexion of the coffin joint with a broken hoof pastern axis. As for how club feet get to be that way in the first place there are several possibilities.
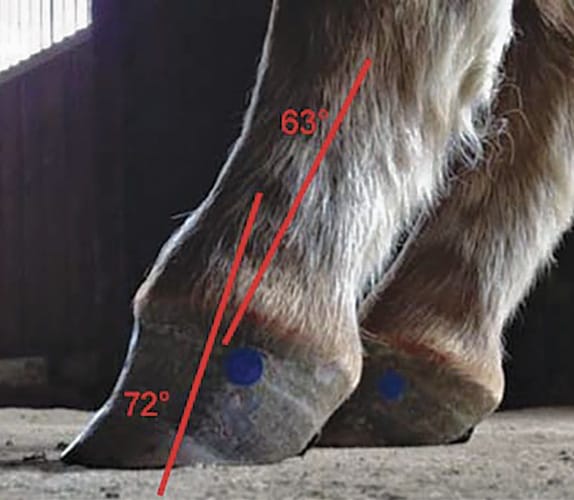
Club feet are surprisingly common with up to 60 of the domestic horse population exhibiting at least minor characteristics. Club foot is a condition of an increased hoof angle above 60 degrees. But what causes it.
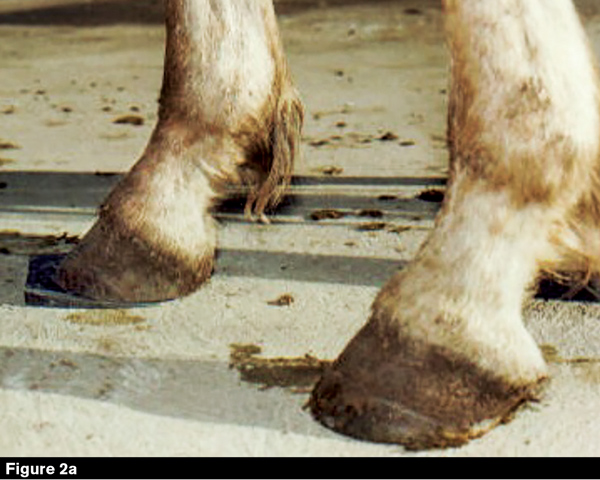
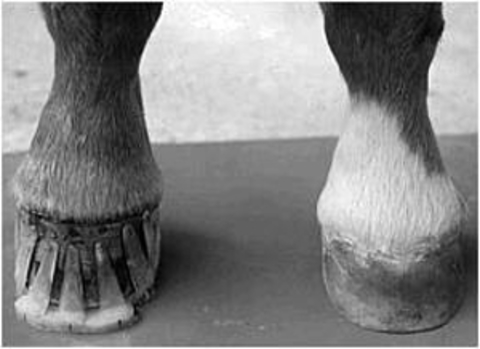
Telltale signs of a club foot may include an excessively steep hoof angle a distended coronary band growth rings that are wider at the heels contracted heels and dished toes. Club foot can occur before or after birth in foals. If a horse has a clubbed foot then the foals that mare or stud produces will have one as well.
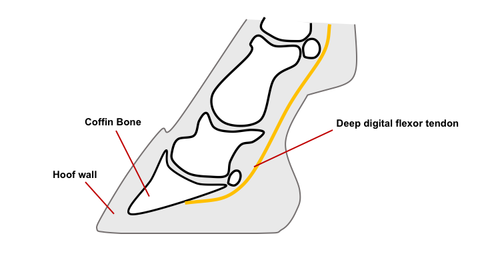
Club foot can develop in mature horses too for similar reasonsany injury or chronic pain that causes a horse to consistently favor one foot can lead to contracting and shortening of the muscles and tendons specifically the deep digital flexor tendon and muscle apparatus in that leg eventually pulling the foot into a more upright position. Risk factors Boys are about twice as. Causes of Club Foot in Horses The deep flexor tendon is shorter than the bones causing a pulling on the coffin bone in the hoof which causes a deformity in the shape of the hoof Congenital deformity at birth occurring within the mares uterus likely due to multiple factors.
Cause it bears little resemblance to the clubfoot de-formity in children referred to as congenital talipes equinovarus45 Presumably the term was coined to describe the upright or straight tubular appear-ance of the foot where there is little expansion of the hoof capsule giving a club-like appearance but. A foals bones growing. Foaling trauma foal grazing stance overly fast growth of limbs injury or even something as benign as over zealous cosmetic trimming of the toes of a foals hooves.
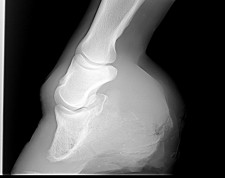
Horses affected with club foot develop a flexural deformity of the coffin joint due to a shortening of the musculotendinous unit that starts high up in the limb and inserts on the coffin bone in the foot resulting in an upright conformation of the foot. Caused by abnormal contraction of the deep digital flexor tendon a club foot puts pressure on the coffin joint and initiates a change in a hoofs biomechanics. Most club feet start very early in the horses life either as a congenital limb deformity already present at birth or as an apparently acquired limb.
The characteristics of a flexure limb deformity commonly referred to as club foot are easy to identify. Club foot refers to a tendon flaw that causes the hoof to be very upright. An extremely high hoof angle is often classified as a club foot Some horses with extremely upright pasterns may be falsely identified as having a clubfoot.
Club feet can also be due to a pain response. Normally were talking about the front pair of hooves. If its painful for the horse to put weight on that limb or favors it a little bit the flexor muscles eventually contract and pull the heel up with the horse walking more on the toe.
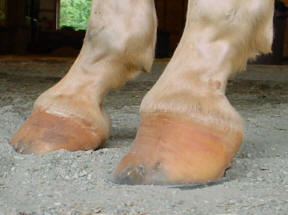
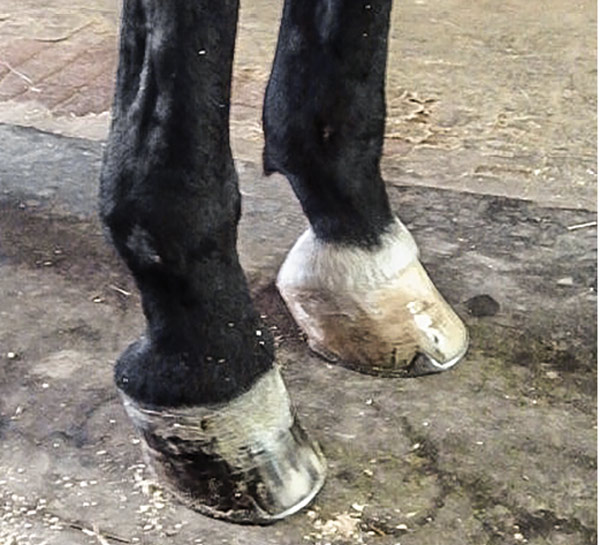
A club-footed horse is defined by most people as a horse with one hoof that grows more upright particularly at the heel angle than its mate on the other side. The primary one is genetics. Growth rings are wider at the heel the toe is usually dished the hoof is high on the heel and the coffin joint axis is broken forward.
It causes the heel to lose contact with the ground and the horse will appear to be walking on tiptoe. Often club foot affects both front legs with one being more severe than the other. This in turn may cause increased stress on the soft tissue structures associated with the navicular bone and may delay the speed of breakover.
Therefore the term club foot in horses does not apply in these cases. Club foot is a term commonly used to describe an abnormally upright front foot conformation. Many folks have treated it as a hoof problem and worked to make the pair of hooves match each other but it is my opinion.
Most horses only have one club. Confidence Building For Horse And Rider Problem Horses Pony Rides Beginner Riding Lessons for Adults Showing Timid Riders Natural Horsemanship Training Horse Sales All Level Riders Family-Friendly Rates Horse Leases Group Lessons Hunter Jumper Training Equine Assisted Psychotherapy Childrens Riding Lessons Working Student Program Starting. After birth foals acquire club feet when the bones grow faster than the tendons.
Causes of club foot Club foot has several possible causes. What Can You Do About Uneven Hoof Growth. Though you will find adults with a club foot that are sound it is recommended that foals that.
After more than 50 years of experience as. The cause of clubfoot is unknown idiopathic but it may be a combination of genetics and environment. A high hoof angle causes coffin joint.
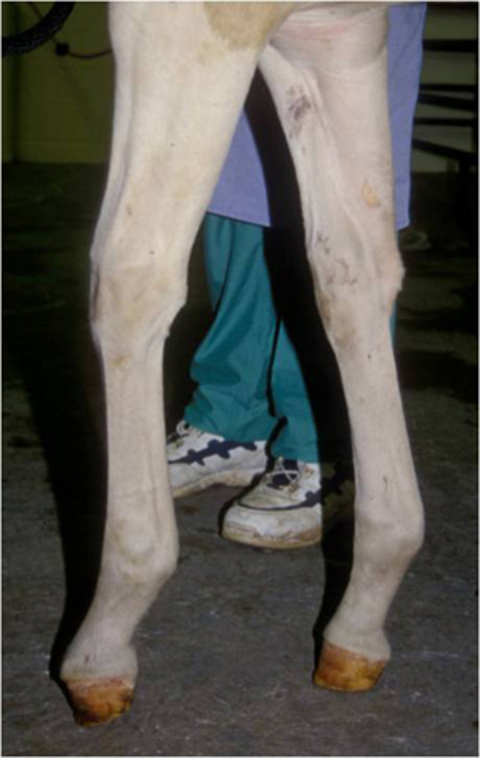
Club foot is one of the most common deformities in the horse world. When a club foot conformation is acquired in the adult horse it is almost always secondary to an underlying cause or disease such as an injury that results in a non-weight bearing lameness excessive trimming of the toe resulting in solar pain chronic low. Any event that leads the young horse to load its weight unequally on its front limbs puts a foal at risk for developing deformities.
It can be a congenital born this way or developmental acquired early. It has even been said that horses which have a leaning posture or are in fact one-. There are several causes of club foot.
The differences in growth rates that cause club feet could be the result of a number of factors including too rapid growth diet imbalances inappropriate exercise traumatic injury and inflammatory responses. Radiographs often reveal that the coffin bone is deformed or remodeled. Often the club foot or feet are secondary to OCD lesions in the shoulder for instance says Burns.
Several theories address the potential causes ranging from a genetic predisposition to hoof or body injury to. Equine club foot results when the tendons along the back of a horses limb shorten causing a constant upward pull where they connect to the coffin bone and heel structure. Some cases likely have a genetic component as certain bloodlines seem to produce more individuals with club feet than is typical.

How D That Happen Origins And Remedies For Clubfoot Horse Racing News Paulick Report
Defining And Fixing A Horse S Club Foot
Club Foot In Horses Equine Chronicle

Flexural Deformities In Horses Musculoskeletal System Merck Veterinary Manual
Equine Podiatry Dr Stephen O Grady Veterinarians Farriers Books Articles

Managing The Club Foot The Horse Club Foot Horses Horse Care

The Club Foot Is It No Big Deal Or A Deal Breaker
Club Foot In Horses Equine Chronicle
What Advice Has Been Most Helpful When You First Encounter A Club Foot